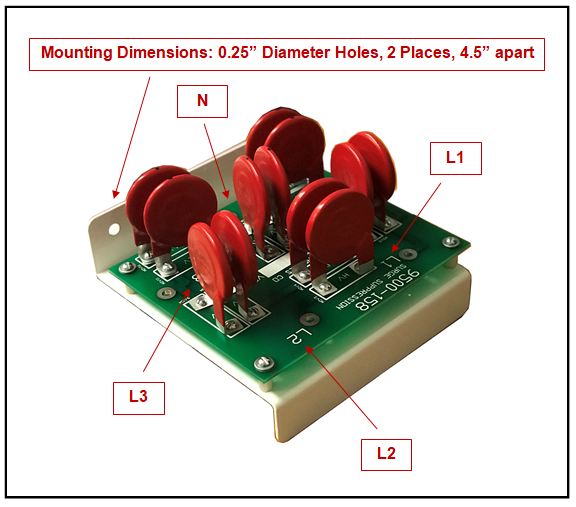
A surge suppressor assembly, often referred to as a surge protector or surge suppressor, is an electrical device designed to protect electronic and electrical equipment from voltage spikes and transient surges. These voltage disturbances can occur due to lightning strikes, power grid fluctuations, or other sources of electrical interference. A surge suppressor assembly typically consists of several components that work together to safeguard connected devices. Here are the key components and features of a surge suppressor assembly:
-
Metal Oxide Varistors (MOVs): MOVs are the primary components used to suppress voltage surges. They are semiconductor devices that have a high resistance under normal operating conditions but become conductive when subjected to high voltage transients. MOVs divert excess voltage away from the protected equipment and absorb the energy of the surge.
-
Gas Discharge Tubes (GDTs): GDTs are another type of surge protection component. They are small, sealed tubes filled with a special gas. When a voltage surge exceeds a certain threshold, the GDT conducts and provides a low-resistance path to ground, diverting the excess energy away from the connected devices.
-
Thermal Fuses: Some surge suppressor assemblies include thermal fuses as safety mechanisms. If the surge protector becomes overloaded or overheated due to prolonged exposure to surges, the thermal fuse disconnects the surge protector from the power source to prevent fire hazards.
-
Protection Status Indicators: Surge suppressors often include LED indicators that show the status of the protection. These indicators may include “protected,” “grounded,” or “fault” status, allowing users to quickly identify if the suppressor is functioning correctly.
-
Joule Rating: The joule rating of a surge suppressor assembly represents its energy absorption capacity. Higher joule ratings indicate the ability to handle larger surges or multiple smaller surges before needing replacement.
-
Clamping Voltage: The clamping voltage is the maximum voltage level at which the surge suppressor will begin diverting excess energy to protect the connected equipment. Lower clamping voltages are better at providing protection.
-
Number of Outlets: Surge suppressors come in various configurations with multiple outlets to accommodate different devices. Some models offer both standard AC outlets and USB ports for charging devices.
-
EMI/RFI Filtering: Some surge protectors include EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) and RFI (Radio-Frequency Interference) filtering to reduce noise and interference on the power lines, which can improve the performance of sensitive electronic equipment.
-
Response Time: A surge suppressor’s response time is critical. It measures how quickly the surge protector reacts to a voltage spike. Faster response times provide better protection.
-
Circuit Breaker: Some surge suppressor assemblies include a built-in circuit breaker that trips in case of an overload or short circuit, providing additional protection.
-
Mounting Options: Surge protectors may be designed for wall mounting, under-desk mounting, or other installation methods to accommodate different needs.
Surge suppressor assemblies are commonly used to protect computers, home entertainment systems, appliances, and other sensitive electronics from damage caused by electrical surges. When selecting a surge protector, consider factors such as the joule rating, clamping voltage, number of outlets, and the specific needs of the equipment you intend to protect. It’s also important to periodically replace surge suppressors that have absorbed a significant amount of energy or have shown signs of wear to ensure continued protection.