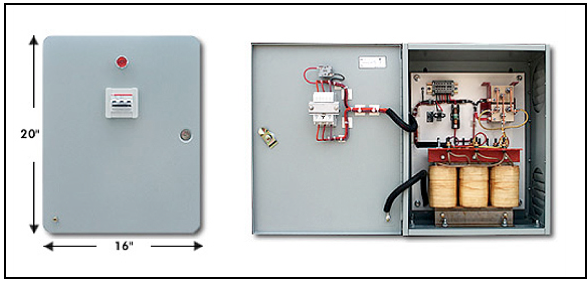
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) machines require specific power supplies to operate effectively. MRI power supplies are critical components that ensure the MRI scanner’s stability, reliability, and safety. Here are some key aspects of MRI power supplies:
-
Power Requirements: MRI machines typically require a substantial amount of electrical power due to the strong magnetic fields they generate and the complex radiofrequency (RF) signal processing involved. MRI power supplies must provide stable and clean power to various components of the scanner.
-
Three-Phase Power: Many MRI machines are powered by three-phase electrical systems. Three-phase power supplies are common in medical facilities and industrial settings because they provide a more efficient and balanced power distribution, which is essential for MRI systems’ consistent operation.
-
High Voltage and Current: MRI power supplies must be capable of providing high-voltage direct current (DC) and/or radiofrequency (RF) power for the superconducting magnets and RF coils used in the scanner. These power supplies must have the capacity to deliver high currents to create the strong magnetic fields needed for imaging.
-
Stability and Precision: The stability of the magnetic field is crucial in MRI imaging to obtain clear and accurate results. Power supplies must maintain precise control over the field strength and compensate for any fluctuations or drift in the magnetic field.
-
Noise and Interference: MRI power supplies must be designed to minimize electrical noise and interference, which can degrade image quality. This includes using well-shielded components and advanced filtering techniques.
-
Safety: Safety is paramount in medical settings. MRI power supplies should comply with stringent safety standards and incorporate features like ground fault protection to ensure the safety of patients and operators. Additionally, they should be designed to minimize the risk of electromagnetic interference with other medical equipment.
-
Backup Systems: Some MRI installations include backup power systems or uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) to ensure that the MRI scanner can continue to function in case of a power outage or other electrical disruptions. These backup systems are essential to avoid downtime and data loss.
-
Cooling: MRI power supplies, particularly those powering superconducting magnets, can generate a significant amount of heat. Adequate cooling systems are essential to dissipate this heat and maintain the system’s performance and safety.
-
Maintenance and Monitoring: Regular maintenance and monitoring of MRI power supplies are crucial to ensure their reliability. Diagnostic tools and remote monitoring capabilities may be included to detect and address potential issues proactively.
-
Integration: MRI power supplies are integrated into the overall MRI system, working in tandem with control systems, imaging software, and other components to create high-quality medical images.
In summary, MRI power supplies play a critical role in the operation of MRI scanners, providing the necessary electrical power to create strong magnetic fields and perform radiofrequency signal processing. These power supplies must meet stringent requirements for stability, precision, safety, and reliability to ensure the effectiveness of MRI imaging in medical diagnosis and research.