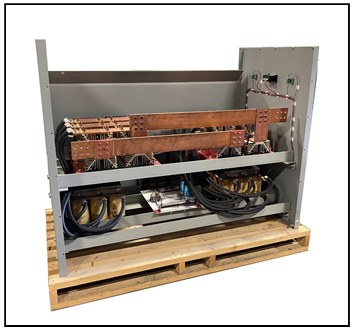
Transformer rectifier assemblies (TRAs) are essential components in various electrical systems, particularly in applications where a stable direct current (DC) power supply is required. They are commonly used in industries such as aviation, telecommunications, railways, and more. A TRA typically consists of two main components: a transformer and a rectifier.
1. Transformer: The transformer in a TRA serves several purposes:
-
Voltage Transformation: The primary function of the transformer is to transform the incoming alternating current (AC) voltage to a different voltage level. This is achieved through the turns ratio of the transformer windings. The secondary winding of the transformer provides the desired output voltage.
-
Isolation: Transformers provide electrical isolation between the input and output sides. This isolation can help protect equipment and personnel from electrical hazards and reduce noise and interference in the system.
-
Impedance Matching: In some cases, transformers are used for impedance matching between the input and output of the rectifier, ensuring efficient power transfer.
2. Rectifier: The rectifier in a TRA converts the alternating current (AC) from the transformer’s secondary winding into direct current (DC). Typically, this is done using diodes, and the most common configuration is a bridge rectifier as described in the previous answer. The rectifier serves the following functions:
-
Conversion: The rectifier converts the AC voltage to DC by allowing current flow in only one direction, effectively removing the negative half of the AC waveform.
-
Smoothing: The resulting DC voltage may still have some ripple or fluctuations. Filtering components like capacitors are often added to smooth the output and provide a more stable DC voltage.
Additional Components and Features:
In addition to the transformer and rectifier, TRAs may include various components and features depending on the specific application:
-
Filtering Capacitors: As mentioned, capacitors are often used to reduce voltage ripple and stabilize the DC output.
-
Voltage Regulation: Some TRAs may incorporate voltage regulation circuits to maintain a constant output voltage even when the input voltage varies.
-
Control and Monitoring: For more advanced applications, TRAs may include control and monitoring systems that allow for remote operation, voltage adjustment, and fault detection.
-
Cooling Systems: In high-power applications, cooling systems such as fans or heat sinks may be integrated to dissipate heat generated during operation.
-
Protection Circuitry: TRAs may also have protection features such as overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, and short-circuit protection to ensure the safety and reliability of the system.
Transformer rectifier assemblies are crucial in various industrial and commercial settings where a stable and reliable source of direct current is required. They are customized based on the specific voltage and current requirements of the application and play a fundamental role in the functioning of many electrical systems.